How to Incorporate More Protein in Your Diet
1. Why Protein Matters for Overall Health Protein isn’t just for muscle—it’s essential building blocks for enzymes, hormones, immune cells, hair, and even healing tissue. Experts recommend 0.8g–1.2g per kg of body weight daily, though active individuals may require more. 2. Top Animal-Based Protein Sources Animal proteins are “complete,” meaning they contain all nine essential…
1. Why Protein Matters for Overall Health
Protein isn’t just for muscle—it’s essential building blocks for enzymes, hormones, immune cells, hair, and even healing tissue. Experts recommend 0.8g–1.2g per kg of body weight daily, though active individuals may require more.
2. Top Animal-Based Protein Sources
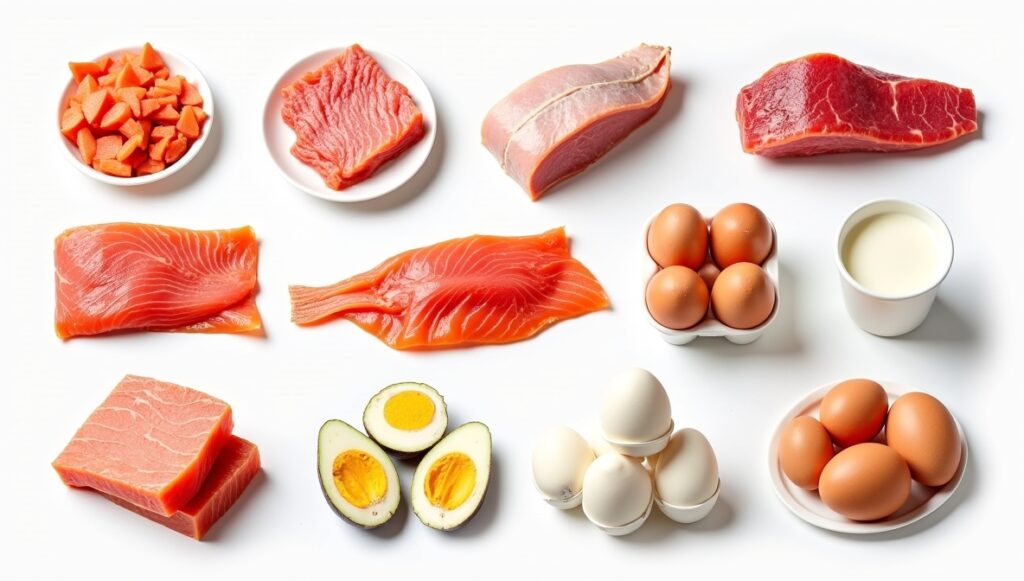

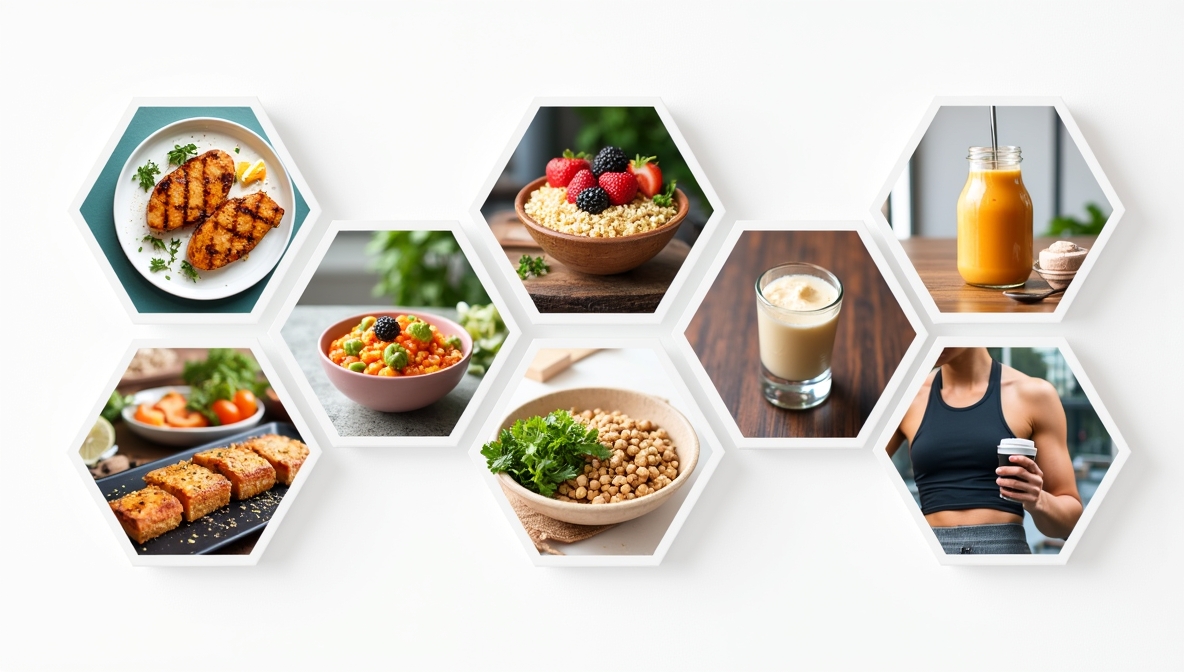
Animal proteins are “complete,” meaning they contain all nine essential amino acids. Include chicken breast, turkey, lean beef, fish (salmon, tuna), eggs, and low-fat dairy in your diet. These pack ~20–30g protein per serving.
3. High-Protein Plant-Based Options
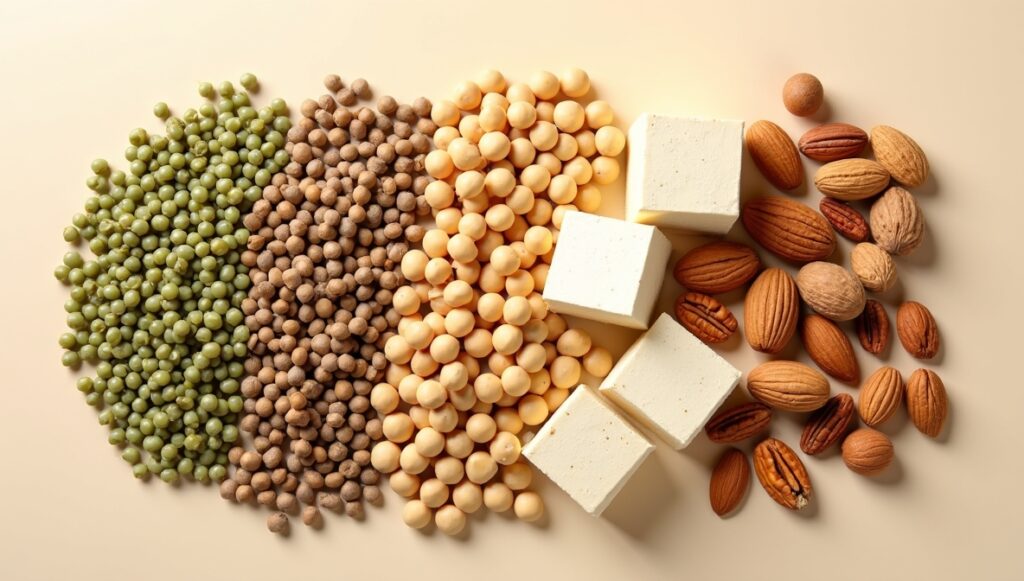

For vegetarians/vegans, plant proteins like tofu, tempeh, lentils, chickpeas, edamame, quinoa, beans, seeds, and nuts are critical. While some lack certain amino acids, smart combos (grains + legumes) create a complete protein profile .
4. Quick, Protein-Rich Snacks
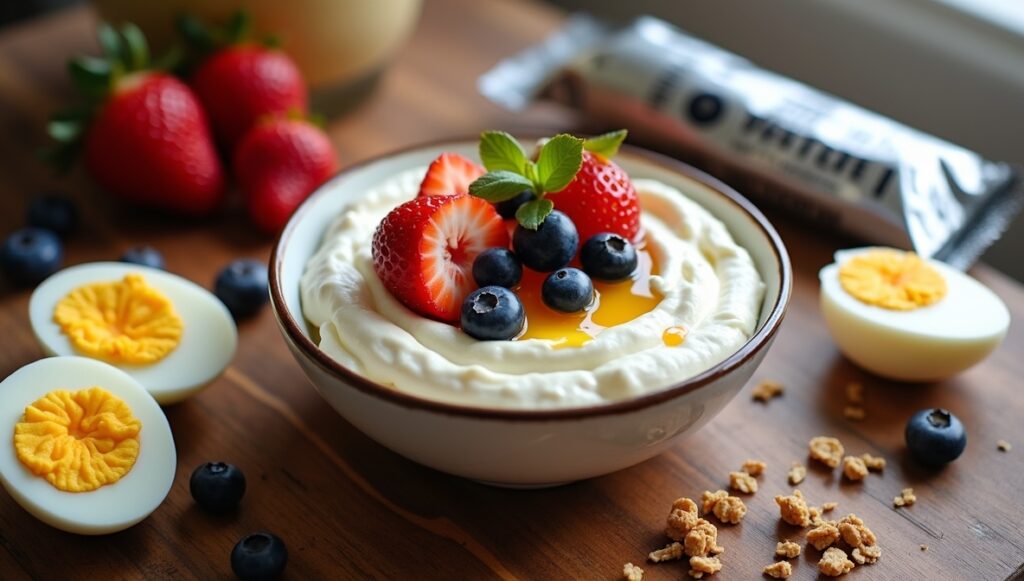

Combat hunger and muscle breakdown with snacks like Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, hard-boiled eggs, edamame, nuts, protein shakes/bars—each providing 10–20g protein and keeping you satisfied between meals.
5. Smart Meal Prep for Protein Goals
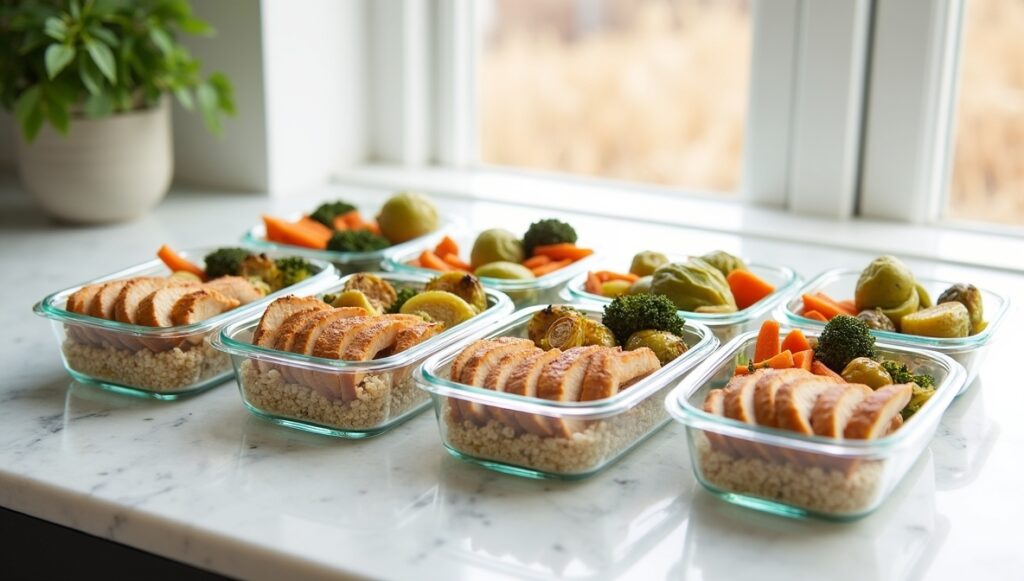

Plan ahead to meet protein targets. Batch-cook lean meats or plant proteins, and portion into containers with veggies and grains. This reduces decision fatigue, saves time, and ensures consistently high protein intake.
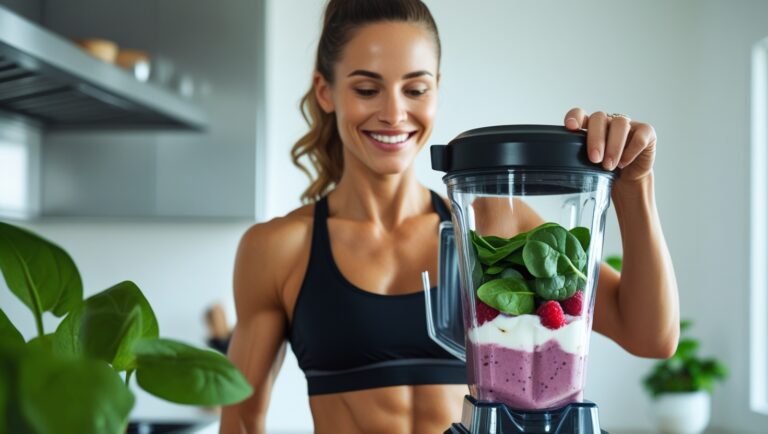
6. Protein-Packed Smoothies & Shakes
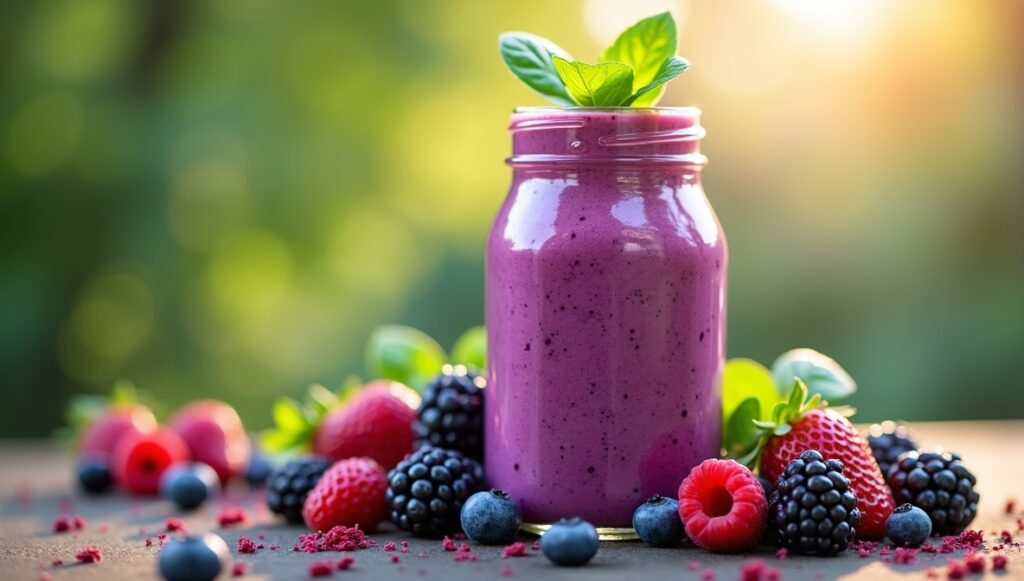

Blending protein powder, Greek yogurt, tofu, or nut butter with fruits and veggies is a convenient and customizable protein booster (15–30g per serving). Ideal for breakfast or post-workout replenishment.
7. Balancing Meals: Protein at Every Meal
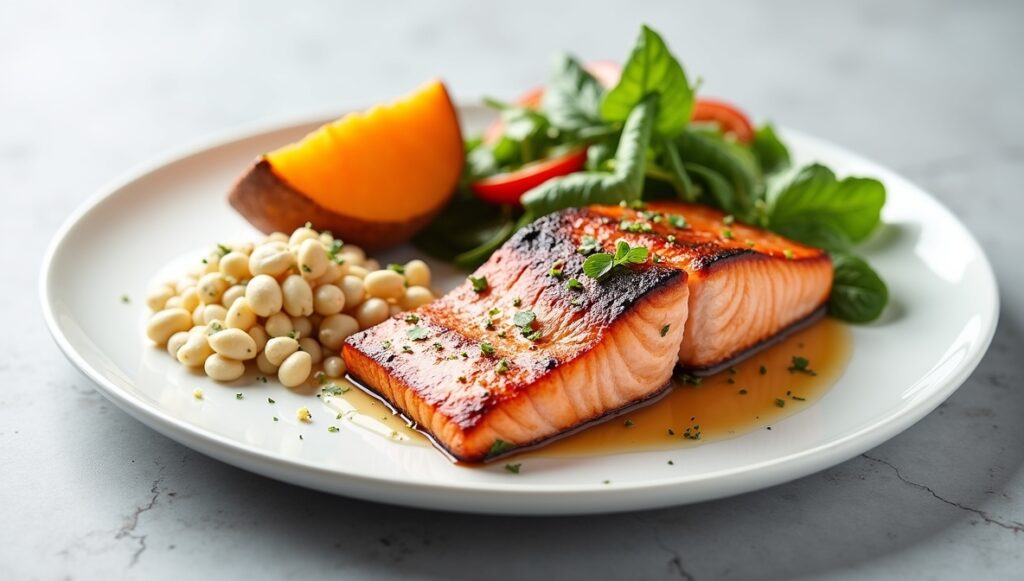

For sustained energy, aim to include 20–30g of protein in each meal—breakfast, lunch, dinner. Balancing with fiber and healthy fats (like avocado, olive oil) improves satiety and nutrient absorption .
8. Addressing Common Misconceptions
Contrary to popular belief:
- More protein ≠ kidney damage in healthy individuals.
- Plant proteins can be as effective as animal sources when varied.
- Protein timing benefits recovery and performance, but total intake matters most.
✅ Final Takeaway
Prioritizing protein at every meal—through lean meats, plant options, snacks, and smoothies—supports muscle, energy, satiety, and overall health. Coupled with meal prep and myth-busting, this blueprint helps you consistently meet your protein goals with ease.






